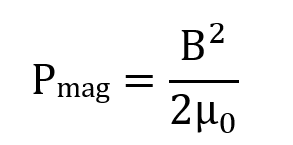MagLev Technology and the Lifts of the Future
Contents |
Introduction
MagLev, or magnetic levitation, has recently started to be used for public transportation across the world. Although more expensive to construct than traditional transportation, MagLev does not require any moving parts and it allows for smooth and quiet transportation. Without the constraints of dry friction, MagLev allows for travel across a guideway containing magnets for stability, lift, and propulsion.
Technology
Magnetic forces counteract gravity and other acceleration forces. Magnetic levitation provides both stability, ensuring that the transportation system remains in the right position and does not flip, and lifting forces that counteract gravity.
Magnetic pressure is defined to calculate the amount of lift, which is done through the following equation:
Pmag represents the force per unit area, in Pascals, B represents the magnetic field in Teslas, and μ0 represents the permeability of vacuum.
The stability factor means that, any displacement as small as it is, away from a stable equilibrium will cause a net force that will push it back to the equilibrium point. Electronic stabilisation, or diamagnetic materials, are stable along at least one axis and have the potential for stability along all axes. Earnshaw's theorem has conclusively proven that paramagnetic, static, and macroscopic fields alone can’t provide stable levitation.
MagLev Transportation
With the potential to exceed speeds of 4,000 miles per hour, or 6,400 km/h, MagLev presents a fast method of mass transportation for the future. With sky high buildings being developed, MagLev could be the answer for less expensive solutions that allow engineers to address the challenge of ensuring lifts can rise to the sky.
With lifts that can travel through lift shafts without cables, lifts won’t need to adapt to the building design. MagLev presents a smaller carbon footprint and can also transport approximately 45% more passengers than other lifts.
Lifts are dispatched much quicker, with the traditional ‘up and down’ system no longer limiting lift design. Destination dispatch technology will also ensure that multi-lift installations in buildings provide an optimised lift use.
Selecting the floor or even the building of destination will be easier, with lifts picking up passengers efficiently according to where they want to go. This technology will also provide a major benefit while utilised alongside MagLev technology, completing transforming how lifts are designed, installed, and used.
--Nathan Massey 15:31, 24 Aug 2017 (BST)
Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Access and inclusion in the built environment: policy and guidance.
- Considerations When Installing a Residential Lift.
- Disabled access lifts.
- Firefighting lift.
- Lift motor room.
- Lift Standards: EN 81-20 and EN 81-50.
- Lifting device.
- Lifting platform.
- Lifts and Their Special Operating Modes.
- Lifts for office buildings.
- Low pit lifts.
- Megaprojects Set to Explode to 24% of Global GDP Within a Decade.
- The history of lifts.
- The importance of service lifts.
- The science of lifts.
- The world’s fastest mode of transport could soon be here.
- The world's fastest lifts.
- Types of lift doors.
- Wheelchair platform stairlifts.
Featured articles and news
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.